|
Weight Loss Surgery
LapBand
How Weight Loss Surgery Reduces Weight?
Am I a Candidate for Weight Loss Surgery?
Is Weight Loss Surgery for You? Are you: * unlikely to lose weight or keep weight off long-term with nonsurgical measures? * well informed about the surgical procedure and the effects of the weight loss surgery? * determined to lose weight and improve your health? * aware of how your life may change after the operation (adjustment to the side effects of the operation, including the need to chew food well and inability to eat large meals)? * aware of the potential for serious complications, dietary restrictions, and occasional failures related to weight loss surgery? * committed to lifelong medical follow-up and vitamin/mineral supplementation? Remember: There are no guarantees for any method, including surgery, to produce rapid weight loss and maintain it. Success with weight loss surgery is possible only with maximum cooperation and commitment to behavioral change and medical follow-up and this cooperation and commitment must be carried out for the rest of your life. A decision to have bariatric surgery is very personal and very important. It will change your life in an irreversible way for the most part, not just because of the quick weight loss it produces. Being careful with a decision like this is the right thing to do. You should research the various weight loss surgeries and the various surgeons. Then you and the surgeon should, together, agree that weight loss surgery is the best choice you can make. Considerations prior to weight loss surgery: * Can you comply with the therapy and follow up that is so necessary after weight loss surgery? You have to follow the directions of your surgeon, especially diet, exercise, labs and office follow up. The surgery is a tool only. Rapid weight loss and maintenance depends on your use of this tool. It would be disastrous if one depends on the surgery alone to take care of the obesity. There will never be a break in following the guidelines set forth by your surgeon regarding diet, exercise and follow up. You are making a life-long commitment. * Are you considering weight loss surgery for the right reasons? Do you just want to look better? Bariatric surgery is NOT done for cosmetic reasons. It is always done to improve failing health. If you meet the medical criteria, you are considering weight loss surgery for health reasons. Feeling better is the goal, looking better is a nice side effect. * Have you made many attempts at weight loss? Only you can decide if you have reached the point where you have exhausted all other options to lose weight. You are making a serious decision that only YOU can make, once you feel you are well informed about the risks and benefits of weight loss surgery. * Are you comfortable with your decision? Are you apprehensive? Once you are feeling comfortable with your decision to make a lifestyle change forever and you know you can do it, you are ready. If you know exactly and feel comfortable with how the weight loss surgery rearranges your digestive system and the short and long-term risks of bariatric surgery, you are ready. If you have found a surgeon that you feel very comfortable with, you are ready. If you are apprehensive about the whole process, you are normal!
Types of Weight Loss Surgeries Restrictive Weight Loss Surgeries
Purely restrictive operations only limit food intake and do not interfere with the normal digestive process. To perform the operation, doctors create a small pouch at the top of the stomach where food enters from the esophagus. At first, the pouch holds about 1 ounce of food and later may stretch to 2-3 ounces. The lower outlet of the pouch is usually about ¾ inch in diameter or smaller. This small outlet delays the emptying of food from the pouch into the larger part of the stomach and causes a feeling of fullness, thus resulting in rapid weight loss in most patients.
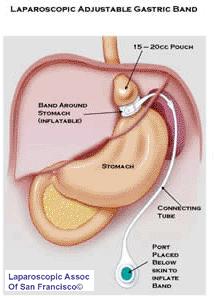
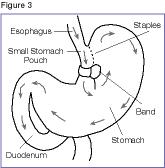
1. Adjustable Gastric Banding (also known as the LAP-BAND) In this procedure, a hollow band made of silicone rubber is placed around the stomach near its upper end, creating a small pouch and a narrow passage into the rest of the stomach. The band is then inflated with a salt solution through a tube that connects the band to an access port placed under the skin. It can be tightened or loosened over time to change the size of the passage by increasing or decreasing the amount of salt solution.
Disadvantages of this weight loss surgery:
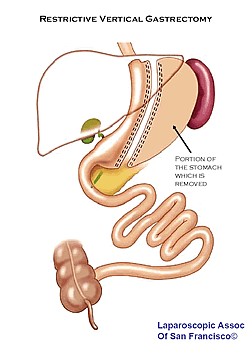
For additional support and information about this surgery visit the Lap-Band? Forum 2.Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy (also called vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy, Greater Curvature Gastrectomy, Parietal Gastrectomy, Gastric Reduction and even Vertical Gastroplasty) is performed by approximately 15 surgeons worldwide. The originally procedure, conceived by Dr. D Johnston in England, was called The Magenstrasse and Mill Operation. It generates rapid weight loss by restricting the amount of food that can be eaten (removal of stomach or vertical gastrectomy) without any bypass of the intestines or malabsorption. The stomach pouch is usually made smaller than the pouch used in the Duodenal Switch.
Advantages of this weight loss surgery:
Disadvantages of this weight loss surgery:
For additional support and information about this surgery visit the Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy Forum
Advantages of this weight loss surgery:
Disadvantages of this weight loss surgery:
For additional support and information about this surgery visit the Vertical Banding Forum Advantages/Disadvantages Overview
Advantages: Restrictive weight loss surgeries are easier to perform and are generally safer than malabsorptive operations. AGB is usually done via laparoscopy, which uses smaller incisions, creates less tissue damage, and involves shorter operating time and hospital stays than open procedures. Restrictive weight loss surgeries can be reversed if necessary, and result in few nutritional deficiencies. Risks: One of the most common risks of restrictive operations is vomiting, which occurs when the patient eats too much or the narrow passage into the larger part of the stomach is blocked. Another is slippage or wearing away of the band. A common risk of AGB is breaks in the tubing between the band and the access port. This can cause the salt solution to leak, requiring another operation to repair. Some patients experience infections and bleeding, but this is much less common than other risks. Between 15 and 20 percent of VBG patients may have to undergo a second operation for a problem related to the procedure. Although restrictive operations are the safest of the bariatric procedures, they still carry risk in less than 1 percent of all cases, complications can result in death. Because combined weight loss surgeries result in greater weight loss than restrictive operations, they may also be more effective in improving the health problems associated with severe obesity, such as hypertension (high blood pressure), sleep apnea, type 2 diabetes, and osteoarthritis. Combined Restrictive/Malabsorptive Weight Loss Surgeries
Combined operations are the most common bariatric procedures. They restrict both food intake and the amount of calories and nutrients the body absorbs.
Advantages of this weight loss surgery:
Disadvantages of this weight loss surgery:
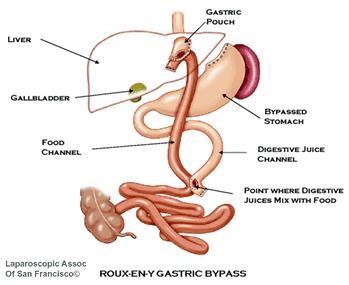
Note (figure 4): This is the RNY without the stomach being transected or divided. This type RNY is not widely done anymore. Most surgeon perform the RNY with the stomach divided with no staple line. Transected means: stomach is completely separated from the new stomach
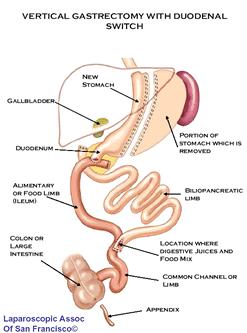
For additional support and information about this surgery visit the Roux-en-Y Forum 2. Duodenal Switch (also called vertical gastrectomy with duodenal switch, biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch, DS or BPD-DS) is performed by approximately 50 surgeons worldwide. It generates weight loss by restricting the amount of food that can be eaten (partial gastrectomy (i.e., partial removal of the stomach along the outer curvature see diagram) and by limiting the amount of food (specifically fat) that is absorbed into the body (intestinal bypass or duodenal switch). This weight loss surgery is more controversial because it has a significant component of malabsorption (bypass of the intestinal tract), which seems to augment and help maintain long-term weight loss. Of the procedures currently performed for the treatment of obesity, it has some powerful and effective components. Due to concerns of possible long-term effects of malabsorption and the technical difficulty involved with this type of weight loss surgery, many surgeons don't perform it.
Advantages of this weight loss surgery:
Disadvantages of this weight loss surgery:
For additional support and information on this surgery visit the Duodenal Switch Forum To locate a Duodenal Switch surgeon in your area click here 3. Biliopancreatic Diversion (BPD) (see figure 5) In this more complicated combined weight loss surgery, the lower portion of the stomach is removed. The small pouch that remains is connected directly to the final segment of the small intestine, completely bypassing the duodenum and the jejunum. Although this procedure leads to weight loss, it is used less often than other types of operations because of the high risk for nutritional deficiencies. This surgery is not commonly done anymore.
Advantages of this weight loss surgery:
Disadvantages of this weight loss surgery:
Advantages/Disadvantages Overview Advantages: Most patients lose weight quickly and continue to lose for 18 to 24 months after the procedure. With the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, many patients maintain a weight loss of 60 to 70 percent of their excess weight for 10 years or more. With BPD/DS, most studies report an average weight loss of 75 to 80 percent of excess weight. Because combined operations result in greater weight loss than restrictive operations, they may also be more effective in improving the health problems associated with severe obesity, such as hypertension (high blood pressure), sleep apnea, type 2 diabetes, and osteoarthritis. Disadvantages: Combined procedures are more difficult to perform than the restrictive procedures. Such weight loss surgeries are also more likely to result in long-term nutritional deficiencies. This is because these weight loss surgeries causes food to bypass the duodenum and jejunum, where most iron and calcium are absorbed. Menstruating women may develop anemia because not enough vitamin B12 and iron are absorbed. Decreased absorption of calcium may also bring on osteoporosis and related bone diseases. Patients must take nutritional supplements that usually prevent these deficiencies. Patients who have the biliopancreatic diversion procedure must also take fat-soluble (dissolved by fat) vitamins A, D, E, and K supplements. RGB and BPD operations may also cause “dumping syndrome,” an unpleasant reaction that can occur after a meal high in simple carbohydrates, which contain sugars that are rapidly absorbed by the body. Stomach contents move too quickly through the small intestine, causing symptoms such as nausea, bloating, abdominal pain, weakness, sweating, faintness, and sometimes diarrhea after eating. Because the duodenal switch operation keeps the pyloric valve intact, it reduces the likelihood of dumping syndrome. Risks with these weight loss surgery procedurs:In addition to risks associated with restrictive procedures such as infection, combined operations are more likely to lead to complications. Combined operations carry a greater risk than restrictive operations for abdominal hernias (up to 28 percent), which require a follow-up operation to correct. The risk of hernia, however, is lower (about 3 percent) when laparoscopic techniques are used. As with any surgery, there can be complications. This list can include:
Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgery This technique is often used for Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, and although less common, biliopancreatic diversion can also be performed laparoscopically. The small incisions result in less blood loss, shorter hospitalization, a faster recovery, and fewer complications than open operations. However, combined laparoscopic procedures are more difficult to perform than open procedures and can create serious problems if done incorrectly.
Weight Loss Surgery for Adolescents
Weight loss surgery is a highly personal decision; it is also a medical decision. Your doctor should discuss the risks and help you measure the probability of benefits so that you can make an informed decision Always get the advice from your attending surgeon on the best surgical option for you. Information provided here is to give an understanding on the different surgery types available. Obesity Help strives to be the top weight loss site on the Web by providing you with helpful and complete information about weight loss surgery, but the advice of your attending surgeon should always supercede anything you learn here. |

 email to a friend
email to a friend printer-friendly version
printer-friendly version